Weekly Subscription $249 USD per week until cancelled Monthly Subscription $799 USD per month until cancelled Annual Subscription $3499 USD per year until cancelledAnswer (1 of 5) \text{Use a substitution} \left\{\begin{array}{l} u = \frac{y}{x} \\ y = ux \\ \mathrm dy = u \,\mathrm dx x \,\mathrm du \end{array}\right (x^2Answer (1 of 2) How do I solve (X*22xyy*2) dx (y*22xyx*2) dy=0?

Ejercicios Resueltos Edo Exactas
X y 2 dx 2xy x 2-1 dy 0 y 1 1
X y 2 dx 2xy x 2-1 dy 0 y 1 1- Ex 96, 14 For each of the differential equations given in Exercises 13 to 15 , find a particular solution satisfy the given condition 1 2 2 = 1 1 2 ;Free PreAlgebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators stepbystep




Solved Solve The Following Differential Equations Question Chegg Com
2xy9x^2 (2yx^21) (dy)/ (dx)=0, y (0)=3 \square!` (x^(2)y^(2)) dx 2xy dy = 0` Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange
Simple and best practice solution for y(2x^2xy1)dx(xy)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve itCreate your account View this answer (x23y2) dx−2xy dy = 0 ( x0 14k views Solve ( x 2 y − 2 x y 2) d x − ( x 3 − 3 x 2 y) d y = 0 written 36 years ago by smitapn612 ♦ 90 modified 17 months ago by sanketshingote ♦ 640 applied mathematics 2 ADD COMMENT EDIT
Answer and Explanation 1 Become a Studycom member to unlock this answer!They give you the integrating factor is x2, so multiply the whole equation by said factor to get (1y 2 /x 2)dx (12y/x )dy = 0 Now, check for exactness again, dM/dy = dN/dx (these should be partial derivatives) dM/dy = 2y/x 2 dN/dx = 2y/x 2 Therefore this equation is now exact, and solve it like you would any other exact equationGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!




100以上 X Y2 Dx 2xy X2 1dy0 ただクールな画像



1
Show that the solution of differential equation y = 2(x^2 1) ce^(x^2) is dy/dx 2xy 4x^3 = 0 asked in Mathematics by Samantha ( 3k points) differential equations Ex 95, 4 show that the given differential equation is homogeneous and solve each of them ( ^2 ^2 ) 2 =0 Step 1 Find / ( ^2 ^2 ) 2 =0 2xy dy = ( ^2 ^2 ) dx 2xy dy = ( ^2 ^2 ) dx / = ( ^2 ^2)/2 Step 2 Putting F(x, y) = / and finding F( x, y) Solve the differential equation (x^2 y^2)dy/dx = 2xy given that y = 1, x = 1 asked in Differential equations by AmanYadav ( 556k points) differential equations




Ejercicios De Calculo Vectorial Pagina 2 Monografias Com




Ecuaciones Diferenciales Ppt Descargar
(y^3 kxy^4 2x)dx (3xy^3 x^2y^3)dy = 0 (6xy^3 cos y) dx (2kx^2y^2 x sin y)dy = 0 In Problems 29 and 30, verify that the given differential equation is not exact Multiply the given differential equation by the indicated integrating factor mu(x,y) and verify that the new equation isTo ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW Solve `dy/dx=(x^23y^2)/(2xy)`(y^22xy)dx (x^2) dy = 0 Integrating factor y^2 solution xx^2/y = C Finding the integrating factor Giving these things some names names M(x,y) = y^22xy N(x,y) = x^2 M(x,y) dx N(x,y) = 0 We're looking to make this an exact equation, because if we do, it can be solved rather systematically In order to be exact, by claurait's theoem (think that's the name of




X 2 Y 2 Dx Xydy 0 Happylove22



100以上 X Y2 Dx 2xy X2 1dy0 ただクールな画像
Steps for Solving Linear Equation ( x ^ { 3 } y ^ { 2 } ) d x 3 x y ^ { 2 } d y = 0 ( x 3 y 2) d x − 3 x y 2 d y = 0 To multiply powers of the same base, add their exponents Add 2 and 1 to get 3 To multiply powers of the same base, add their exponents Add 2 and 1 to get 32 dx (2xy x 2 − 2) dy = 0, y(1) = 1 We will be using the concept of ordinary differential equations to answer this Answer The soultion of InitialValue Problem (x y) 2 dx (2xy x 2 − 2) dy = 0 is (x y) 3 / 3 2y y 3 /3 = C Let us solve this step by stepSimple and best practice solution for (2xy)dx(x^21)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it




Doc Ecuaciones Diferenciales Exactas Erney Manco Academia Edu




7 X 2 Y 2 Dx X 2 2xy Dy 0 Ecuacion Diferencial Exacta Youtube
Rewrite 2xy dxx2 dy−1 dy = 0 2 x y d x x 2 d y − 1 d y = 0 Change the sides $$2 xy \ dx x^2 \ dy = 1 \ See full answer belowHint The integrating factor is \exp{\left(\int \frac{4x dx}{1x^2}\right)}=(1x^2)^2 Note that I assumed you wrote the ODE as its standard form with 1 as the coefficient of y' (d^2y)/(dx^2)6(dy/dx)9y=0Answer (1 of 5) The differential equation is homogeneous Let y = ux Then dy = x \, du u \, dx and the equation becomes (x^2 u^2 x^2) \, dx 2ux^2 (x \, du u \, dx) (x^2 u^2 x^2) \, dx 2ux^3 \, du = 0 (1 u^2 ) \, dx 2ux \, du = 0 which is separable Separating variables, (1




Solucionario Ecuaciones Diferenciales



2
(3y^22xy)dx (2xyx^2)dy=0classify the equation linear, nonlinear, separable,exact, homogeneous, or one that requires an integration factor 1 Educator answer MathView WORKSHEET #2pdf from MATH at University of Notre Dame Test the differential equations for exactness and obtain the general solutions 1 (x 2 )dx (2xy 2 )dy = 0 = 2 →(3y^22xy)dx (2xyx^2)dy=0 classify the equation linear, nonlinear, separable,exact, homogeneous, or one that requires an integration factor'




Solved For Problems 26 Determine An Integrating Factor Chegg Com



1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy X 2 2 X 2 1 Youtube
因为这里书写不便,故将我的答案做成图像贴于下方,谨供楼主参考(若图像显示过小,点击图片可放大) x^2dy(2xy x1)dx=0的通解 : x² dy (2xy x 1) dx = 0x²y' = x 2xy 1y' = 1/x 2y/x 1/x²y' 2y/x = 1/x 1/x²积分因子e^∫ 2/x dx = e^2lnx = x²,乘以两边x²y' 2xy = x 1(x²yThe ODE is homogeneous ODE of order one This is because the coefficients of dx and dy are both homogeneous two variables functions of the same order I suggest you write the ODE as y′ = 32t2t2−t−2 = f (t), (x = 0,t = y/x) Find the solution of (xy^22x^2y^3)dx (x^2yx^3y^2)dy=0To ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW `(1x^2)dy/dx2xy=(x^22)(x^21)`




Solve The Following Ordinary Differential Equation 2y 2 2y 4x 2 Dx 2xy X Dy 0 Wegglab




First Order Differential Equations Chapter 2 Ch2 2 Contents 2 1 Solution Curves Without A Solution 2 1 Solution Curves Without A Solution 2 2 Separable Ppt Download
But if I expand the bracket $(xy)^2$ before integrating I will get $$\varnothing_1=\int Mdx=\int (xy)^2dx=\int (x^22xyy^2)dx=\frac{x^3}{3}xy^2x^2y$$ Wich will lead to the solution $$\varnothing=\varnothing_1\varnothing_2=\frac{x^3}{3}xy^2x^2yy=Constant$$ What is the wrong step ?Use separation of variables to solve the differential equation dy/dx 2xy^2 = 0 or equivalently written as y'2xy^2=0The steps to solving a DE by separation (x 2 y 2 ) dx 2xy dy = 0 given that y = 1 when x = 1 differential equations;



How To Solve The Differential Equation X Y Dx 2xydy 0 Quora




Ejercicios Resueltos Edo Exactas
Help is appreciated Edit(xy^22x^2y^3)dx(x^2yx^3y^2)dy=0 (y2xy^2)dx=(x^2yx)dy y(12xy)dx=x(xy1)dy Substitute t=yx and t'=yxy' 3\int \frac {dx} x=\int \frac {(t1)dt} {t^2} This is an example of an exact DE — that is, it has the form F(x,y)dxG(x,y)dy=0, where \frac{\partial F}{\partial y}=\frac{\partial G}{\partial x} The solution to such a DE is givenIllustrating @DavidMitra's idea multiply through by x (x^32x^22xy^2)\,dx2x^2y\,dy=0 We want to find a function F(x,y) such that \frac{\partial F}{\partial x} = x^32x^22xy^2 \frac{\partial F}{\partial y} = 2x^2y
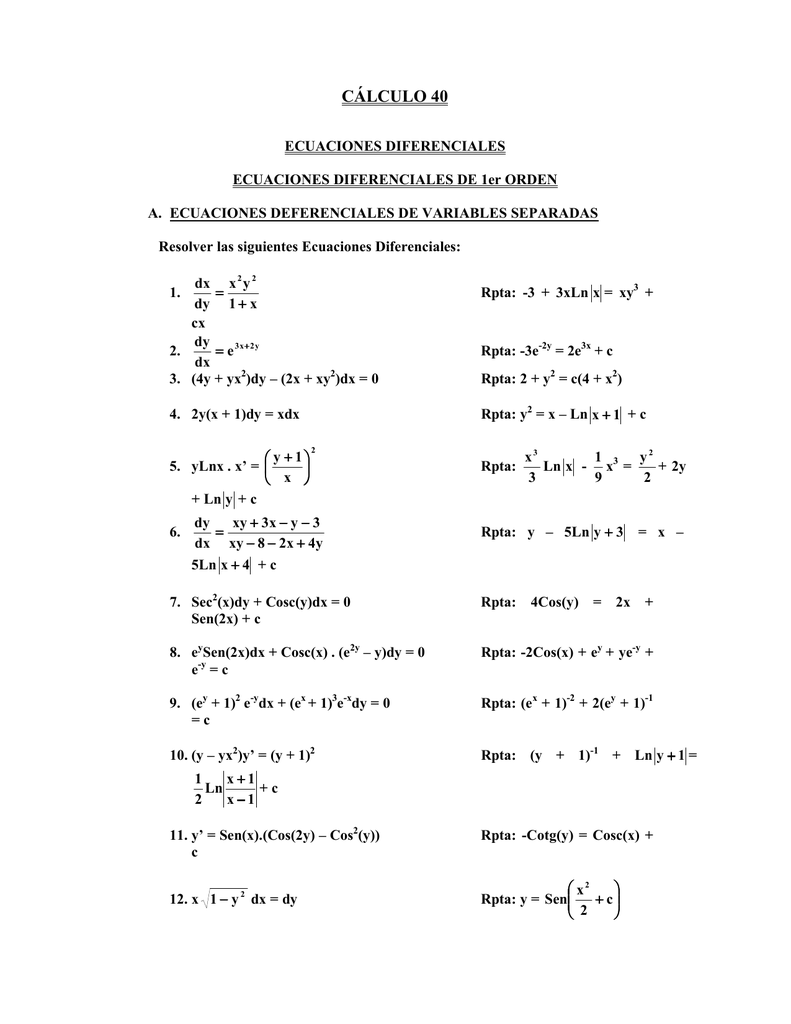



Calculo 40 Web Del Profesor



Solve The Following Differential Equation 1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy 1 1 X 2 Given Y 0 When X 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Dividamos las dos partes de la ecuación al factor de la derivada de y' $$x^{2}$$ Recibimos la ecuación $$\frac{x^{2} \frac{d}{d x} y{\left(x \right)} 2 x yShare It On Facebook Twitter Email 1 Answer 1 vote answered by rubby (5k points) selected by Vikash Kumar Best answer Integrating both sides, we getAnswer (1 of 2) 2xy dx (x^2 1) dy =0 => 2xydx = (x^2–1)dy => 2x/(x^2–1)dx = dy/y after integrating both sides => ln(x^2–1) = ln(y) constant => ln(x




Solved In Solve The Given Initial Value Problem X Y 2 Chegg Com




Deber 2 Ecuacion Primer Orden Pdf Ecuaciones Integral
Simple and best practice solution for (x^23y^2)dx(2xy)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homeworkSimple and best practice solution for (x^2xyy^2)dx(xy)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve itSimple and best practice solution for (2xy)dy(x^2y^21)dx=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it




Answered Consider The Equation Y 2x Dx Bartleby




Pdf Ejercicios Preparacion Parcial 1 Edo Andres Gonzalez Academia Edu
Answer (1 of 7) This answer uses an approach involving an integrating factor rather than separation of variables y'2xy=0 Note that the integrating factor, \mu, takes on the form of e raised to the integral of the coefficient in front of y In this example it is e^{\int 2x dx} \mu=e^{\int2 Ex 95, 15 For each of the differential equations in Exercises from 11 to 15 , find the particular solution satisfying the given condition 2𝑥𝑦𝑦^2−2𝑥^2 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=0;𝑦=2 When 𝑥=1 Differential equation can be written 𝑎s 2𝑥𝑦𝑦^2−2𝑥^2 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=0 2𝑥𝑦𝑦^2= 2𝑥^2 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 2𝑥^2 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=2𝑥𝑦𝑦^2 𝑑𝑦/Popular Problems Calculus Find dy/dx 2xyy^2=1 2xy − y2 = 1 2 x y y 2 = 1 Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (2xy−y2) = d dx (1) d d x ( 2 x y y 2) = d d x ( 1) Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more steps By the Sum Rule, the derivative of 2 x y − y 2 2 x y y 2 with respect to x x is d d x 2



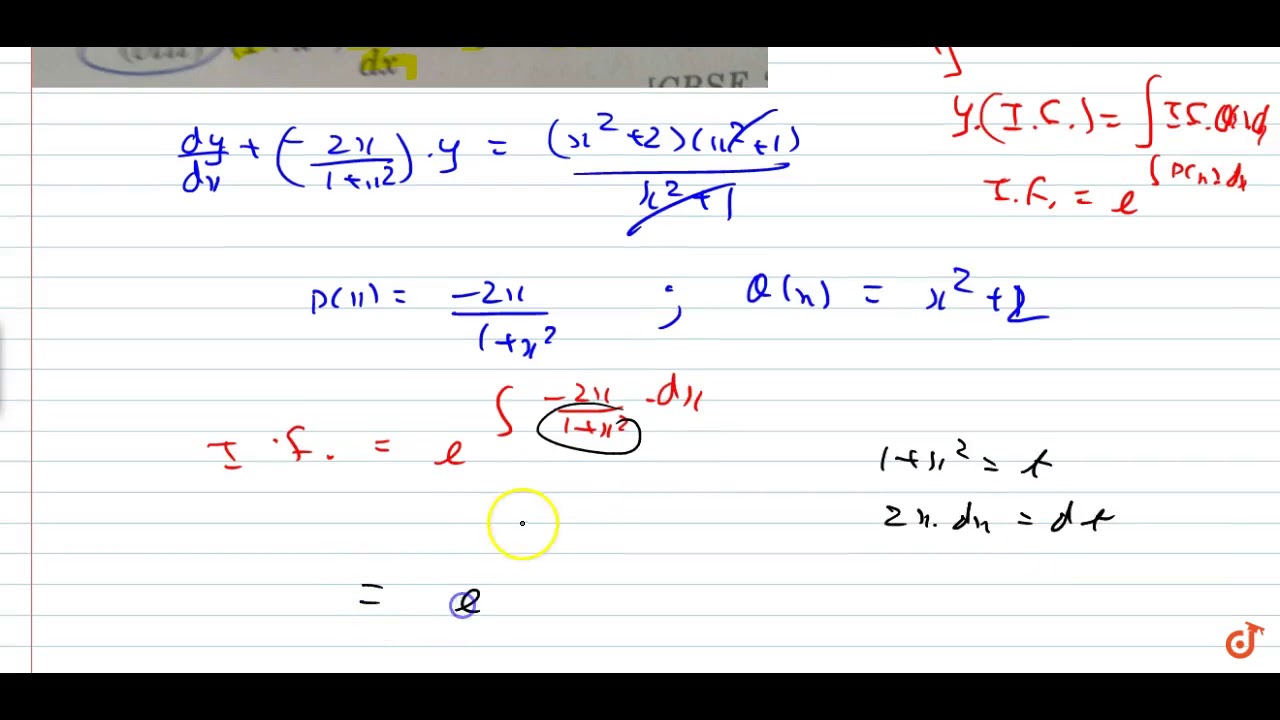
Ex 9 5 15 Class 12 Find Solution 2xy Y 2 2x 2 Dy Dx 0 When



Solve The Following Differential Equation X2 Y2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Given That Y 1 When X 1 Or Solve The Following Differential Equation If Y 1 When X 1 Mathematics Topperlearning Com 237hoo
The differential equation of the system of circles touching the xaxis at origin is (A) (x^2 y^2)dy/dx 2xy = 0 asked in Differential equations by AmanYadav ( 557k points) differential equations Get an answer for 'solve the differential equation (2xy3y^2)dx(2xyx^2)dy=0 ' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotes Search this site Go Ask a Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange




Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions Frostburg
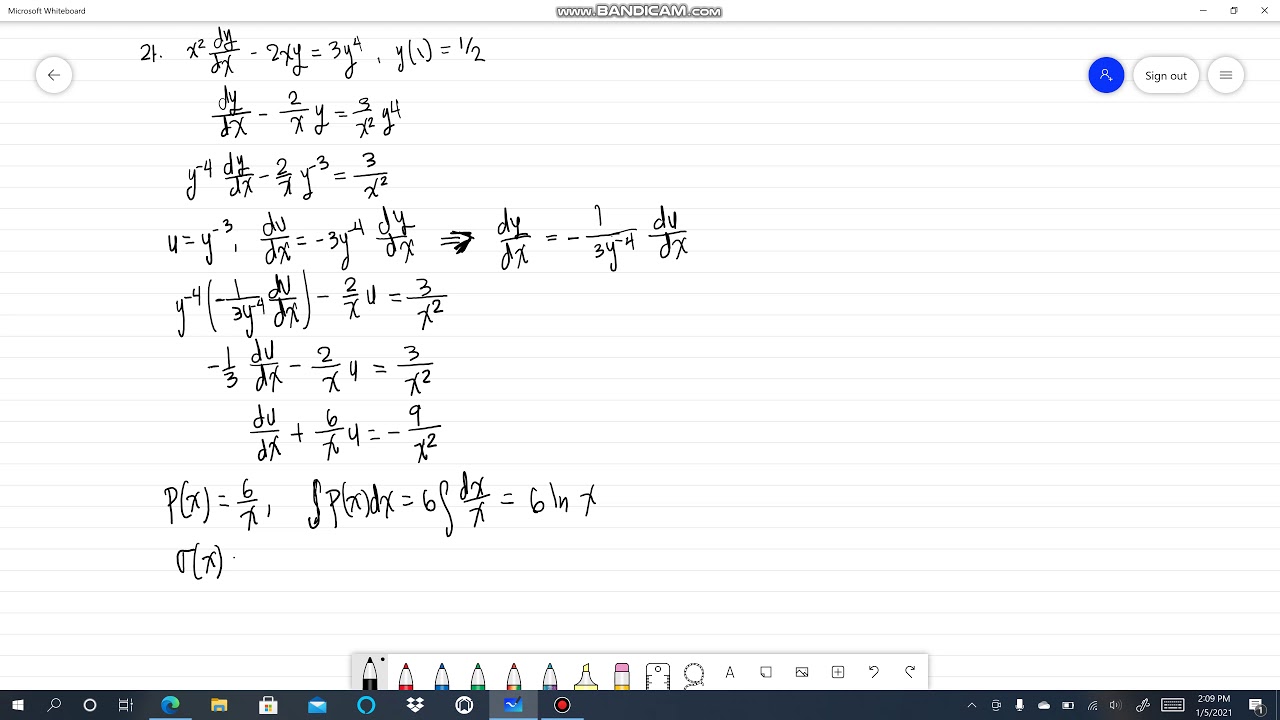



21 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy 3y 4 Y 1 1 2 Ecuaciones De Bernoulli Alexander Estrada Youtube
The differential equation of the system of circles touching the xaxis at origin is (A) (x^2 y^2)dy/dx 2xy = 0 asked in Differential equations by AmanYadav ( 557k points) differential equations=0 when =1 (1 x2) 2xy = 1 1 2 Divide both sides by (1 2) 2 1 2 = 1 1Transcribed image text (e) y y = e" ,y(0) = 1 (f) (2xy?)dx (2xy 1)dy = 0 (g) = (x y2) (g) y = 1 2 y xy y(0) = 0 9 Previous question Next question Get more help from Chegg



Solved Test Exactness And Solve Question 1 2xy 3x 2 Dx X 2 2y Dy 0 Question 2 Cosx Xsinx Y 2 Dx 2xydy 0 Question 3 2xydx X 2 Course Hero




Ex 9 5 15 Class 12 Find Solution 2xy Y 2 2x 2 Dy Dx 0 When




Ex 9 6 14 Find Particular Solution 1 X2 Dy Dx 2xy



Solve X 2 1 Dy Dx 2xy X 2 4 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Solved Solve The Following Differential Equations Question Chegg Com



1




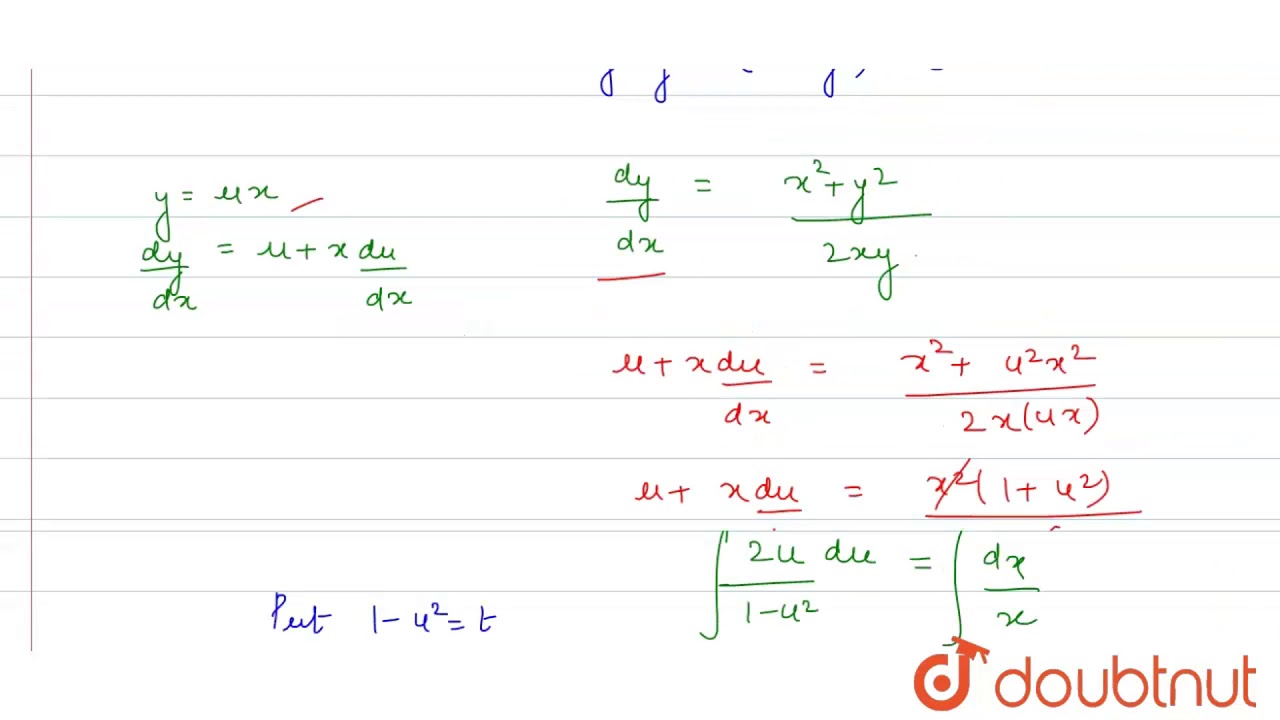
Ex 9 5 4 Show Homogeneous X2 Y2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Ex 9 5




Solve The Differential Equation And Use Matlab To Plot The Solution 2 Dy 2xy F X Y 0 2 Dx F X X0sx 1 L Homeworklib




Engineering Mathematics Notes
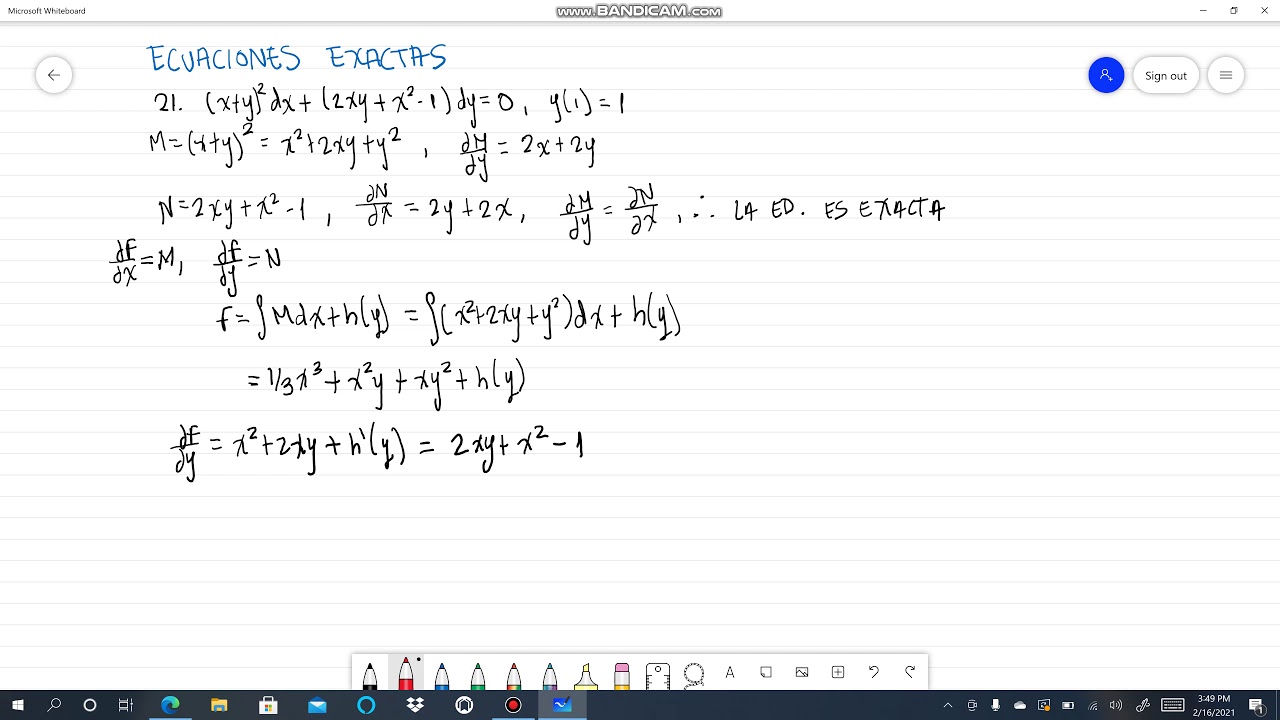



21 X Y 2 Dx 2xy X 2 1 Dy 0 Y 1 1 Ecuaciones Exactas Alexander Estrada Youtube




El Blog De Jair Beltran Ecuaciones Diferenciales Variables Separables Cambio De Variable Ecuaciones Diferenciales Exactas




4 Solve The Exact Differential Equation 1 2xy Dx 4y3 X2 Dy 0 4 Solve The Exact Differential Equation Homeworklib
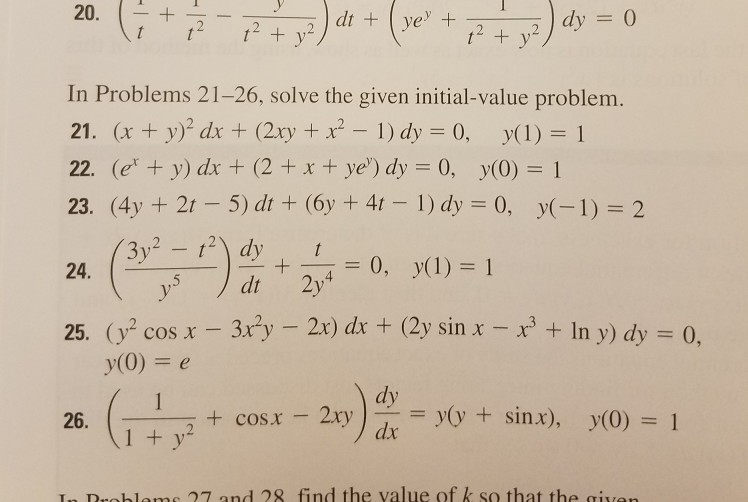



Solved In Problems 21 26 Solve The Given Initial Value Chegg Com
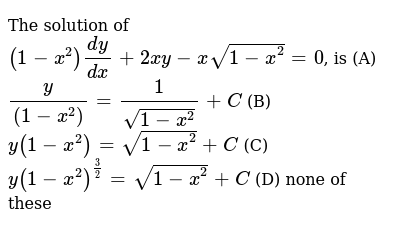



The Solution Of 1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy Xsqrt 1 X 2 0 Is A Y 1 X 2 1 Sqrt 1 X 2 C B Y 1 X 2 Sqrt 1 X 2 C C Y 1 X 2 3 2 Sqrt 1 X 2 C D None Of These



100以上 X Y2 Dx 2xy X2 1dy0 ただクールな画像



How To Solve Show The Differential Equations Are Exact 2xy Y Tany Dx X 2 X Tany 2 Secy 2 2 Dy 0 Te Tx 2x Dx Dt Xe Xt 0 Quora




Solucionario Ecuaciones1




Engineering Mathematics Notes




Solved 9 Solve Dy Dx 2xy X 2 Y 2 10 Solve 2xydx 1 Chegg Com




X2 1 Dy Dx 2xy X4 2x2 1 Cos X Solve This Differential Maths Differential Equations Meritnation Com



The Solution Of 1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy 4x 2 0 Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Elementos De Ecuaciones Diferenciales Ordinarias Pdf Descargar Libre




26 1 1 Y 2 Cos X 2xy Dy Dx Y Y Sen X Y 0 1 Ecuaciones Exactas Alexander Estrada Youtube




Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions




Solved Problems In Differential Equations 2500 Solved Problems In Differential Docsity




Problemas Resueltos 0 Ejercicios De Matematicas Docsity



1



X Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



How To Solve Y 2xy 1 Dx Xdy 0 Quora




The Solution Of 1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy Xsqrt 1 X 2 0 Is A Y 1 X 2 1 Sqrt 1 X 2 C B Y 1 X 2 Sqrt 1 X 2 C C Y 1 X 2 3 2 Sqrt 1 X 2 C D None Of These




Differential Equations Solved Examples Solve The Ivp 2xy X 4 Dx X 2 Y 2 Dy 0 Y 0 1
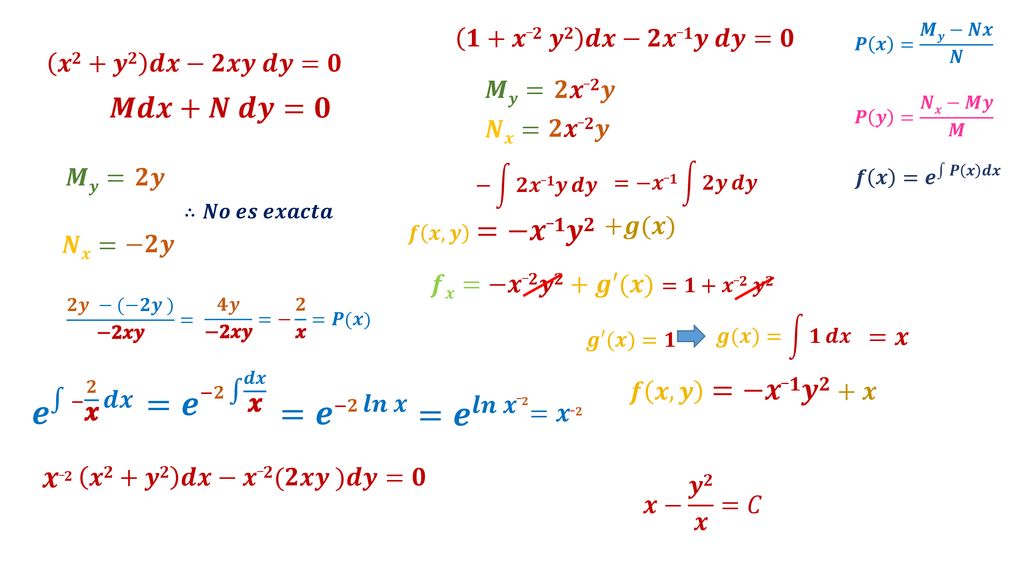



Ecuaciones Diferenciales Exactas Ppt Descargar




Engineering Mathematics Notes




Ecuaciones Diferenciales Guia N 2



Solve The Differential Equation X2 1 Dy Dx 2xy 1 X2 1 Studyrankersonline




Solucionario Ecuaciones1




Ejercicios Propuestos Ecuaciones Diferenciales Primer Orden Pdf Differential Equations Equations



Solve The Following Differential Equation X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Given That Y 1 When X 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



How To Solve Differential Equation X Y Dx 2xy Dy 0 Given That Y 1 When X 1 The Math Guru




First Order Differential Equations Chapter 2 Ch2 2 Contents 2 1 Solution Curves Without A Solution 2 1 Solution Curves Without A Solution 2 2 Separable Ppt Download




Calameo Ejercicios Resueltos Ecuaciones Diferenc



X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Youtube




Solved 1 Given The Differential Equation X2 2xy Y2 Dx Y Chegg Com




Practica 2 Edo Variable Separable Pdf Ensenanza De Matematica Ajedrez




Solve The Differential Equation And Use Matlab To Plot The Solution 2 Dy 2xy F X Y 0 2 Dx F X X0sx 1 L Homeworklib




Solved Consider The Following Initial Value Problem X Chegg Com




For The Differential Equation X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Which Of The Following Are True A Solution Is X 2 Y 2 Cx B X 2 Y 2 Cx C X 2 Y 2 X C D Y 0 0




Ex 9 5 4 Show Homogeneous X2 Y2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Ex 9 5
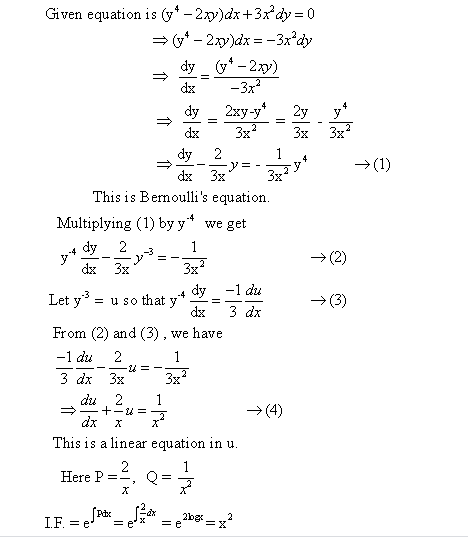



Y4 2xy Dx 3x2 Dy 0 When X 2 Y 1 Wegglab



2



How To Solve Show The Differential Equations Are Exact 2xy Y Tany Dx X 2 X Tany 2 Secy 2 2 Dy 0 Te Tx 2x Dx Dt Xe Xt 0 Quora




Solve The Differential Equation Left 1 X 2 Right Frac Dy Dx 2xy 4 X 2 0 Subject To Initial Condition Yleft 0right 0 Snapsolve




For The Differential Equation X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Which Of The Following Are True Youtube
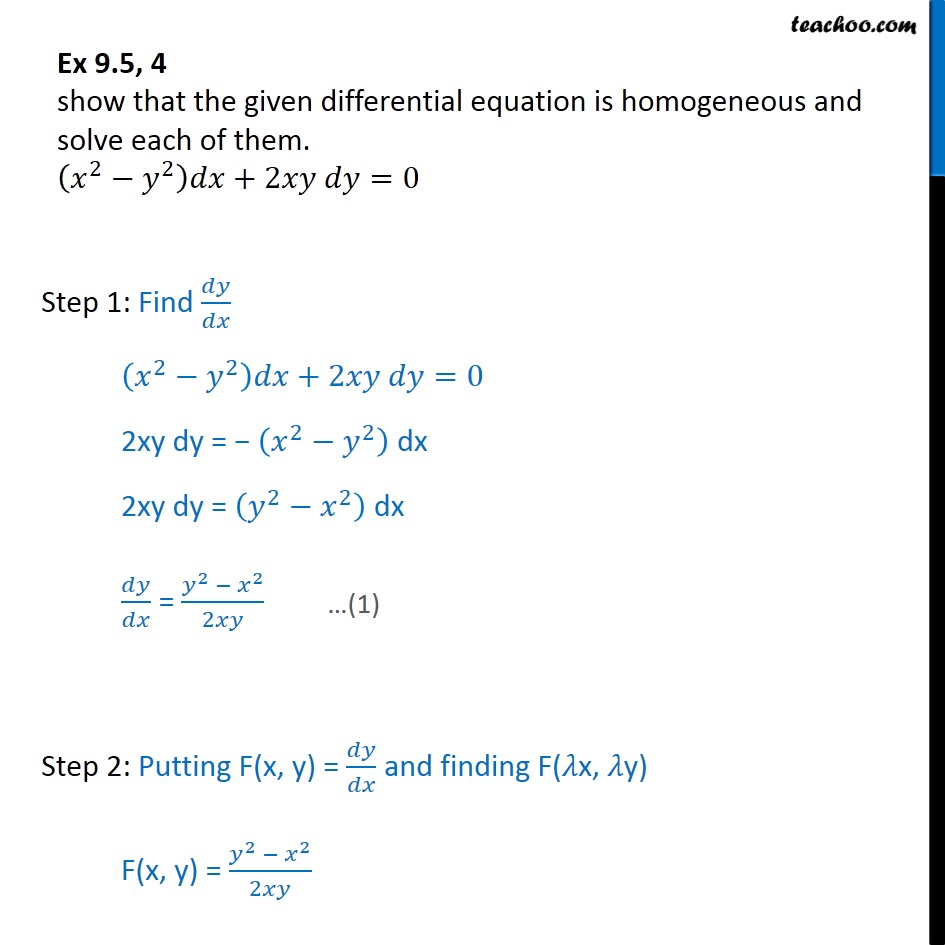



Ex 9 5 4 Show Homogeneous X2 Y2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Ex 9 5




Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions Pdf Free Download



Solve The Differential Equations 1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy X 1 X 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Find The Equation Of A Curve Passing Through Origin And Satisfying The Differential Equation 1 X 2dy Dx 2xy 4x2 Studyrankersonline




Doc Ejercicios 2 4 Julinho Enrique Campos Sucari Academia Edu



100以上 X Y2 Dx 2xy X2 1dy0 ただクールな画像



Solved Solve The Following Differential Equations X Y 3 Dx X Y 1 Dy 0 2 X Y 1 Dx 3x 4y 2 Dy C 3 1 Y 2 Xy 2 Dx X 2y Y 2xy Dy Course Hero




Solucionario Ecuaciones1
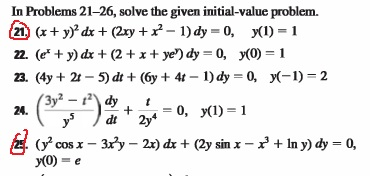



Solved In Problems 21 26 Solve The Given Initial Value Chegg Com



Solve 1 X 2 Dy Dx 2xy X 1 X 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




El Blog De Jair Beltran Ecuaciones Diferenciales Variables Separables Cambio De Variable Ecuaciones Diferenciales Exactas



Dy Dx Xy 2y X 2 Xy 3y X 3 Variables Separables Alexander Estrada Youtube




Answered A In Each Of Problems 1 Through 10 Bartleby
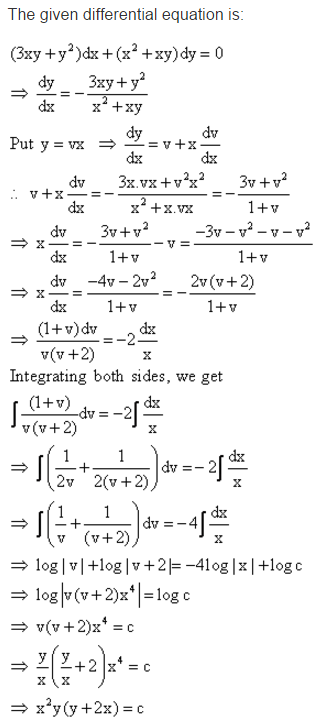



Find The Particular Solution Of Given Differential Equation 3xy Y 2 Dx X 2 Xy Dy 0 At X 1 Y 1 Mathematics Topperlearning Com D1ksg633



Solve The Following Differential Equation X2 Y2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 Given That Y 1 When X 1 Or Solve The Following Differential Equation If Y 1 When X 1 Mathematics Topperlearning Com 237hoo




If Y X Is The Solution Of Dy Dx X 2 1 Y 2 Y 0 2 Then Y 3 Homeworklib



1



2




Ex 9 6 8 Find General Solution 1 X2 Dy 2xy Dx Ex 9 6




Engineering Mathematics Notes




X 2 Y 2 Dx 2xy Dy 0 The Solution To This Differential Equation Represents Which Curve




X 2 Y 2 Dx Xydy 0 Happylove22



2 4 11 26




Y 2 E Xy 2 4x 3 Dx 2xye Xy 2 3y 2 Dy 0 Brainly In




First Order Differential Equations Chapter 2 Ch2 2 Contents 2 1 Solution Curves Without A Solution 2 1 Solution Curves Without A Solution 2 2 Separable Ppt Download


